Imagine having full visibility of your vehicles—every mile logged, every job dispatched, and every driver connected—in real time. Modern real-time fleet web applications make this possible. These tools aren’t just for logistics giants anymore; any business with vehicles or mobile teams can use them. Whether it’s delivery services, field maintenance, or construction, having real-time tracking and management transforms operations.
For a software development agency, building a real-time fleet web application is more than writing software—it’s enabling smarter dispatch, better coordination, and data-driven decisions. This blog will explain what makes a strong fleet application, the key features, architecture, security, performance, and how agencies can help clients improve field operations.
What Is a Real-Time Fleet Web Application?
A real-time fleet web application is an online platform (web or hybrid mobile/web) that gives businesses live insight into their field operations. It allows:
- GPS tracking of vehicles and assets
- Dispatching tasks to drivers or field staff
- Driver and vehicle management (profiles, status, availability)
- Real-time communication between field teams and dispatchers
- Tracking tasks from assignment to completion
- Analytics and reporting on fleet performance
With a good fleet app, organizations reduce idle time, improve on-time delivery, respond faster to issues, and provide transparency to clients or stakeholders.
Core Components of a Fleet Web Application
1. Asset & User Management
A fleet system maintains a database of vehicles/assets and users (drivers, dispatchers, managers). It tracks vehicle identifiers, driver assignments, availability, and maintenance history.
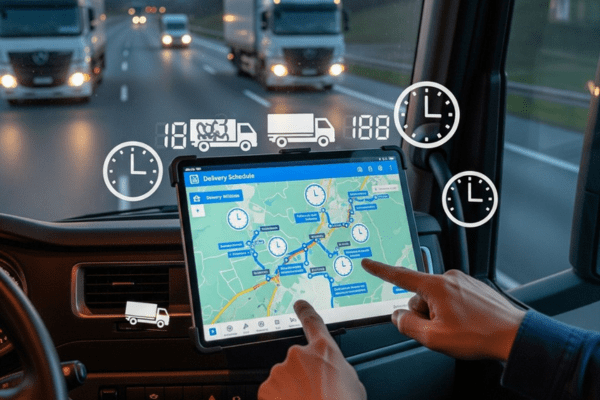
2. Real-Time GPS Tracking & Mapping
Vehicles report GPS coordinates via mobile devices or telematics. A map interface shows locations, routes, and statuses (in transit, idle, completed). The backend must handle frequent location updates, while the frontend renders maps in real time.
3. Dispatch & Workflow System
Dispatchers assign jobs quickly, see vehicle availability, and send tasks. Drivers use mobile interfaces to accept tasks, update status, and mark completion. Workflow states—assigned, en route, arrived, complete—are visible across roles.
4. Communication & Notifications
Real-time chat, push notifications, and alerts for exceptions (breakdowns, delays) keep field teams connected.
5. Analytics & Dashboarding
Metrics like vehicle utilization, trip duration, idle times, and completion rates help managers spot trends, optimize routes, and make strategic decisions.
6. Integrations & Scalability
The system should integrate with maintenance, fuel tracking, billing, customer portals, or third-party telematics. Architecture must handle more vehicles, data, and users as the business grows.
Security & Performance Considerations
- Secure Data Transmission: Use HTTPS/TLS for GPS and status updates.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Drivers, dispatchers, and managers see only what their role allows.
- Data at Rest Protection: Encrypt logs, driver data, and location history.
- Real-Time Data Handling: Backend must support frequent updates with low latency.
- Scalability & Failover: Handle spikes in data or traffic gracefully.
- Audit Trails & Monitoring: Track who changed what and when for compliance.
- User Experience: Mobile apps must work offline and sync efficiently when connectivity returns.
Advanced Features to Enhance Fleet Applications
- Geo-Fencing & Route Optimization: Alerts for vehicles leaving zones; smart route suggestions.
- Predictive Maintenance: Monitor vehicle health and trigger maintenance alerts.
- Client Visibility: Give customers live tracking and ETA updates.
- Mobile Document Capture: Upload proof of delivery, inspect vehicles, or capture job completion data.
- Machine-Learning Analytics: Predict delays, optimize dispatch, analyze driver behavior.
- Multi-Platform & Offline Mode: Ensure web and mobile apps work in low connectivity.
Case Study Reference
A real-world example is Phantom Disposal, where a fleet platform was built with live GPS tracking, dispatch, driver/dispatcher modules, and in-app chat. This solution reduced manual tracking, improved field visibility, and streamlined operations.

real-time fleet web application
Conclusion
A real-time fleet web application is more than maps and job assignments—it transforms field operations into a connected, data-driven system. Live GPS tracking, efficient dispatch, real-time communication, and analytics help organizations reduce costs, improve reliability, and make smarter decisions.
For software agencies, building such platforms is an opportunity to deliver strategic value. With robust architecture, security, scalability, and a user-friendly interface, agencies enable clients to run operations efficiently today and prepare for future growth.